click to enlarge
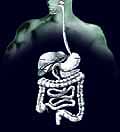
Organs of the Body
The parts of the body for digestion of food include the digestive tube, or alimentary canal, and related organs in the abdomen.
The digestive tube extends from the mouth to the anus. If it were stretched out, it would be about 9 meters long. It is made up of several muscle layers and mucous membranes.
- The esophagus conveys food from the mouth to the stomach.
- The small intestine follows the stomach. It is divided into three parts, the duodenum, the jejunum and the ileum, where digestion is completed and food is absorbed. The ileum empties into the large intestine, which plays a major role in absorption of fluids.
- The large intestine is made up of the cecum , colon, rectum and anal canal.
- The liver and pancreas are two large glands in the abdomen that assist the intestines in the process of digestion.
- The biliary system collects bile from the liver and delivers it into the duodenum. It is made up of the hepatic ducts, common bile duct (CBD), and gallbladder. The CBD passes through the head of the pancreas and joins the pancreatic duct where it empties into the duodenum at the ampulla of Vater.
Several other organs of the body are close to the intestinal tract. These include those in the chest such as: parts of the respiratory tract and associated lymph nodes; the thyroid; the aorta, and other major arteries and veins. Other organs in the abdomen include: the spleen, the adrenal glands, and the kidneys. Major blood vessels include: the aorta and main branches (the celiac and superior mesenteric artery), and the portal venous system (the portal, splenic and superior mesenteric veins). From the rectum and colon, organs in the pelvis can be imaged, such as the prostate and uterus.
Endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) is performed by placing an echoendoscope or catheter into the digestive tube to obtain images of the digestive tube and organs close to it.